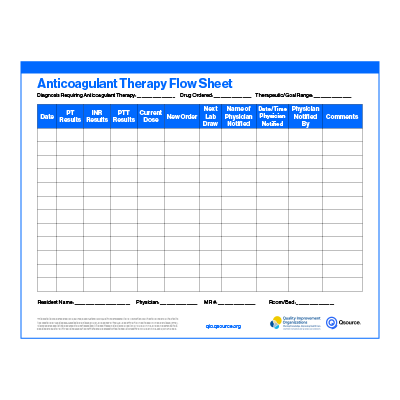
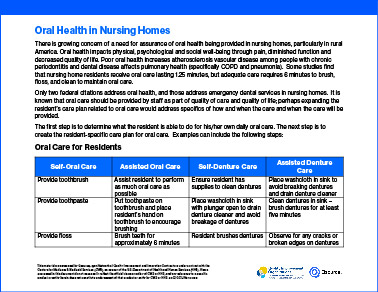
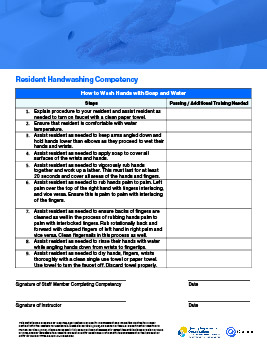
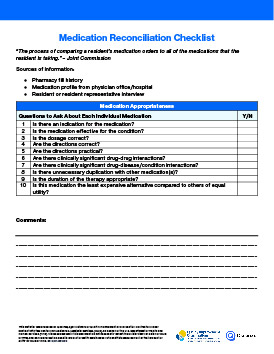
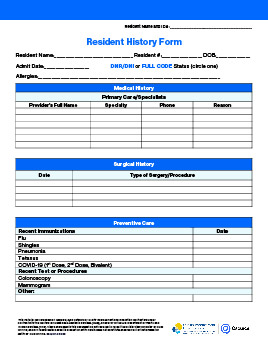
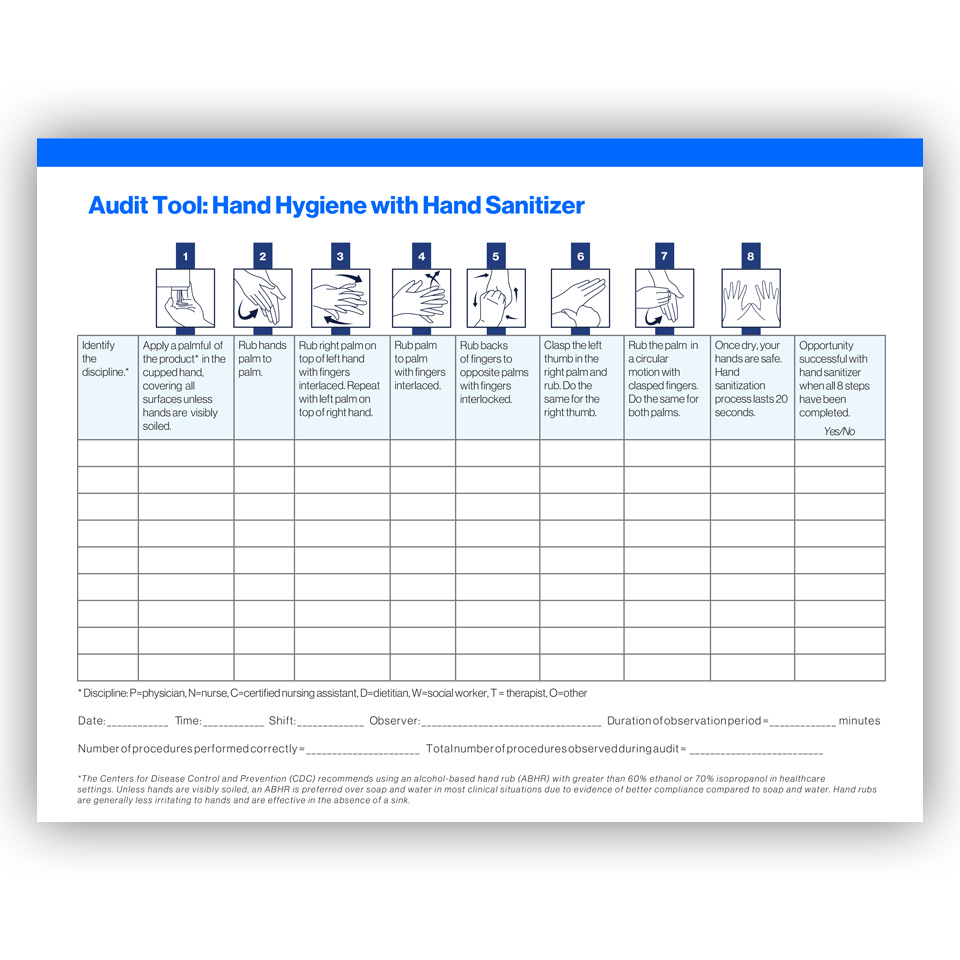
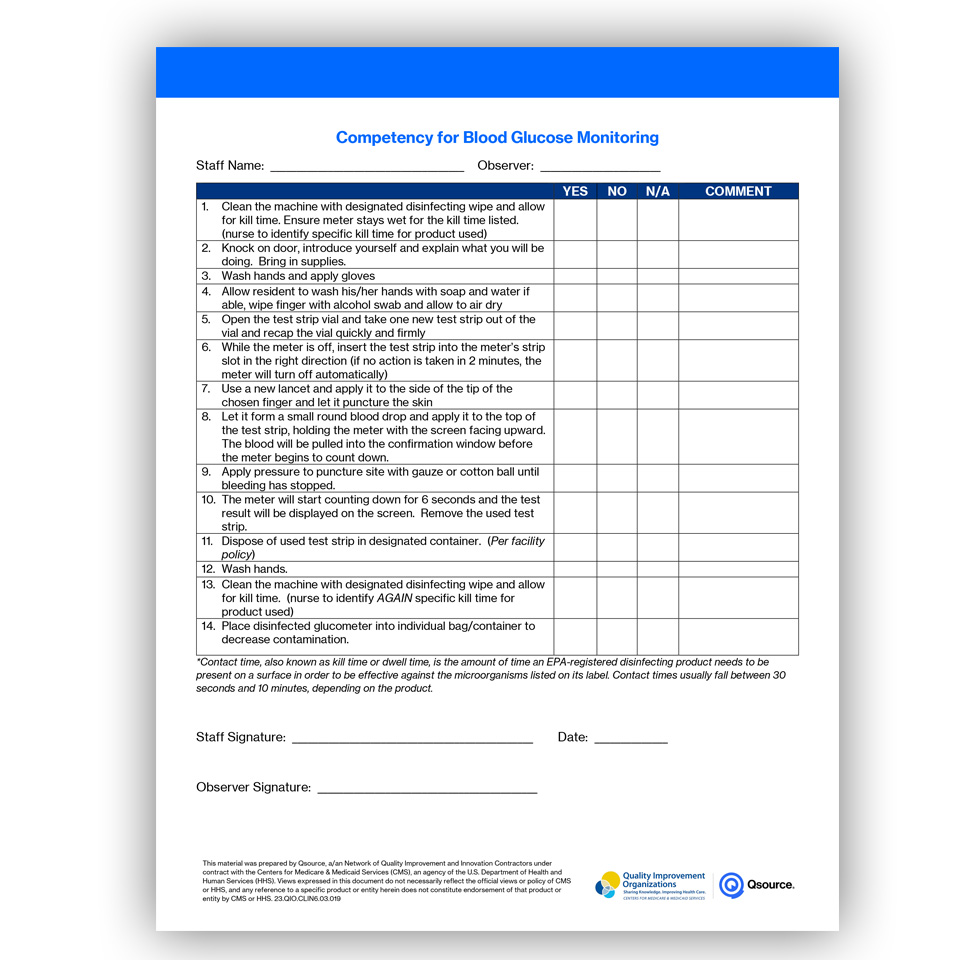
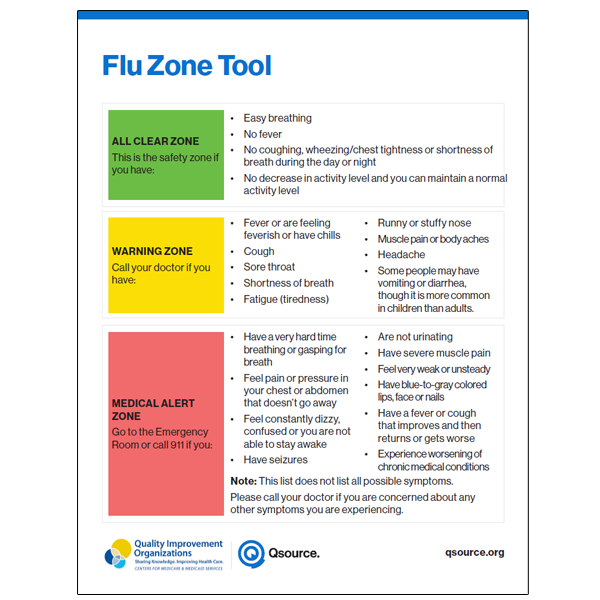
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Includes 5 files
Reducing Restraints Tips
Restraints can cause harm, but there are alternatives. By making informed decisions, we can make resident care safer. Learn about your residents’ physical and emotional needs and individualize their care plans to meet needs. Ask questions about each resident in your care, and for those with restraints, use restraint alternatives when possible.
Antibiotic Stewardship Toolkit for Nursing Homes
Nursing homes are encouraged to work in a step-wise fashion, implementing one or two activities to start and gradually adding new strategies from each element over time. Any action taken to improve antibiotic use is expected to reduce adverse events, prevent emergence of resistance and lead to better outcomes for residents in this setting.
Facility Assessment Tool
The purpose of the assessment is to determine what resources are necessary to care for residents competently during both day-to-day operations and emergencies.
CDI Toolkit
This toolkit should be used by providers and other healthcare professionals working to reduce HAIs. Each section contains information and additional online resources that can be used at any stage of progress.
Readmission Root Cause Analysis Tool – Skilled Nursing Facility
Tool to find the root cause of a nursing home’s problem.
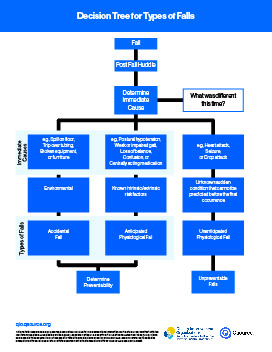
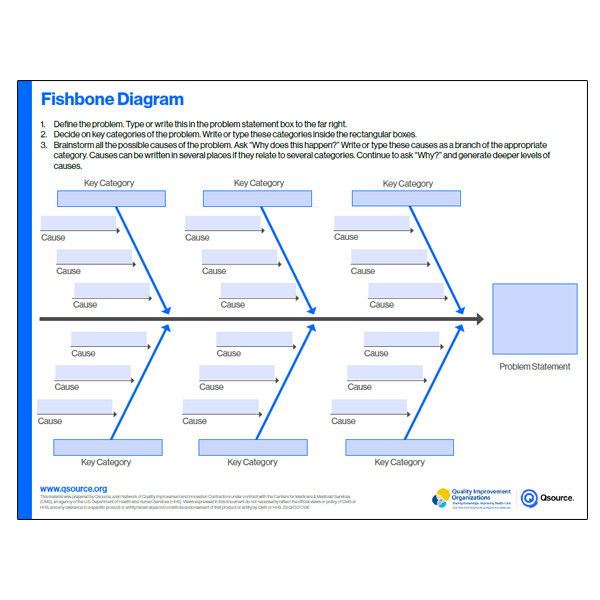
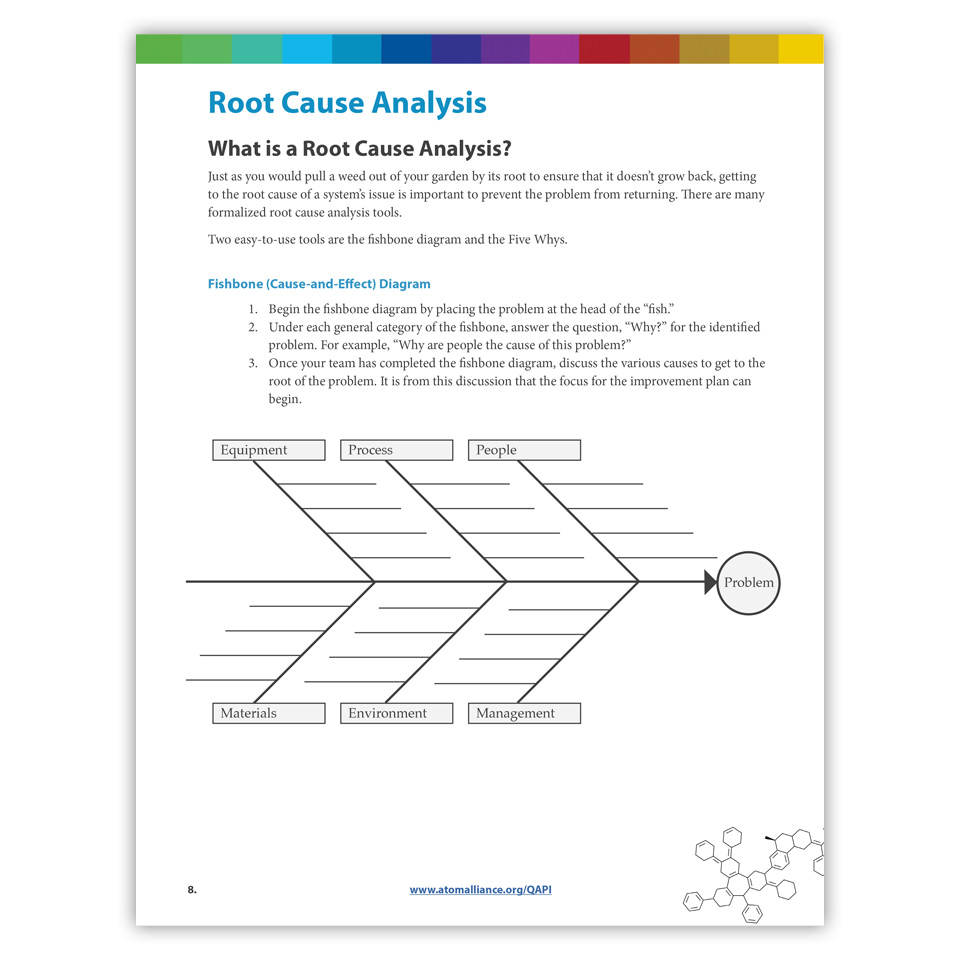
Fishbone Diagram
Getting to the root cause of a system’s issue is important to prevent the problem from returning.
QAPI Companion Guide
This companion guide is designed to help your team recognize and understand the major components of the Quality Assurance/Performance Improvement Initiative (QAPI).
QAPI Plan Outline
This worksheet was designed to work in conjunction with the QAPI Guide for Developing a QAPI Plan. It will help you summarize the QAPI progress you have achieved and create an outline for writing your QAPI plan.
QAPI Step 12: Take Systematic Action
“Weak” interventions often not prevent the recurrence of the original problem. Whenever possible, use strong interventions, suchas simplifying a process or making physical or environmental changes, to “hardwire” the change into the existing system.
QAPI Step 11: Getting to the Root of the Problem
Prevent recurring problems by ensuring that all possible root causes have been identified and addressed. Remember to use systematic tools, such as the fishbone diagram or the “Five Whys” to dig below the surface.
QAPI Step 10: Plan, Conduct, Document PIPs
For those areas that require a PIPs, PIP teams should use a methodic or standardized process for making improvements. PDSA is one well-known model, but there are others that may also work for your organization. e important point is to use a strategic methodology, and not a haphazard, “throw it at the wall and see if it sticks” approach.
QAPI Steps 7-9
Effective use of data will help ensure that decisions are made based on fact, and not on an assumption of the truth. Just as a physician needs data about a patient to diagnose a condition, QAPI teams and PIP teams will need data to ensure they are targeting the right areas.
QAPI Step 4: Identifying Guiding Principles Worksheet
Is the care provided by your facility tied to your organization’s fundamental purpose or philosophy? How do you determine programmatic priorities? Taking time to articulate the purpose, the guiding principles and the scope of QAPI will help you integrate these efforts into your organization.
QAPI Step 2: Teamwork Worksheet
QAPI at a Glance states that QAPI relies on teamwork in several ways. Do teams at your organization have a clear purpose? Do teams have defined roles for each team member to play? Do teams have commitment and active engagement from each member?
QAPI Companion Guide: Steps 1-3 Worksheets
The facility leadership (i.e., medical director, administrator, director of nursing and other key managers) is responsible for setting the tone to help staff identify how to meet the organization’s mission, vision, guiding principles, standards and expectations. Without strong leadership, change efforts often fail or are not sustainable.
Elements of Pressure Ulcer Prevention – A Discussion and Evaluation
Most pressure ulcers are preventable. Here are some elements of pressure ulcer prevention. Read, discuss and answer the questions; then, use your responses as part of a facility pressure ulcer prevention self-evaluation.